| [1] Sensebé L, Krampera M, Schrezenmeier H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for clinical application. Vox Sanguinis. 2010;98:93-107.[2] Cervelló I, Mas A, Gil-Sanchis C, et al. Reconstruction of endometrium from human endometrial side population cell lines. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21221.[3] Beane OS, Darling EM. Isolation, characterization, and differentiation of stem cells for cartilage regeneration. Ann Biomed Eng. 2012;40(10):2079-2097.[4] Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhyan RK, Gerasimov UV. Bonemarrow osteogenic stem cells: in vitro cultivation andtransplantation in diffusion chambers. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1987;20(3):263-272.[5] Nöth U, Rackwitz L, Steinert AF, et al. Cell delivery therapeutics for musculoskeletal regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(7-8):765-783.[6] Holzwarth C, Vaegler M, Gieseke F, et al. Low physiologic oxygen tensions reduce proliferation and differentiation of human multipotentmesenchymal stromal cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2010;11:11.[7] Gronthos S, Zannettino AC, Hay SJ,et al. Molecular and cellular characterization of highly purified stromal stem cells derived from human bone marrow. J Cell Sci.2003; 116(Pt9): 1827-1835.[8] Kuci S, Kuci Z, Kreyenberg H, et al. CD271 antigen defines a subset of multipotent stromal cells with immunosuppressive and lymphohematopoietic engraftment-promoting properties. Hematologica. 2010;95(4):651-659.[9] Zhu H, Guo Z, Jiang X, et al. A protocol for isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse compact bone. Nat Protocols. 2010;5(3):550-560.[10] 杨丽,张荣华,谢厚杰,等.建立大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞稳定分离培养体系与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(6):1064-1068.[11] 刘天阳,周学平.破骨细胞分化因子及信号转导通路与中医药对其分化的干预抑制作用[J].安徽医药,2012,16(2):146-149.[12] Mori M, Sadahira Y, Awai M. Characteristics of bone marrow fibroblastic colonies (CFU-F) formed in collagen gel. Exp Hematol. 1987;15(11):1115-1120.[13] 解琳娜,王健民,邱慧颖,等.小鼠间充质干细胞培养扩增后生物学特性研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2007,15(3):542-546.[14] Bianco P, Robey PG, Simmons PJ. Mesenchymal stem cells: revisiting history, concepts, and assays. Cell Stem Cell. 2008; 2(4):313-319.[15] 栗扬阳,赵庆华.不同因子影响骨髓间充质干细胞的多向分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(23):4299-4305.[16] 赵大成,汪玉良,党跃修,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在组织工程研究中的应用进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(49): 9271-9274.[17] Cheng L, Qasba P, Vanguri P, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells support mefakaryocyte and pro-platelet formation. J Cell Physiol. 2000;184(1):58-69.[18] Neuhuber B, Swanger SA, Howard L, et al. Effects of plating density and culture time on bone marrow stromal cell characteristics. Exp Hematol. 2008;36(9):1176-1185.[19] 李晓峰,赵劲民,苏伟,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(10):1721-1725.[20] 蔡鹏,朱绍兴,苏一鸣,等.全骨髓贴壁法分离培养大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞及其诱导分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(36):7073-7077.[21] Polisetti N, Chaitanya VG, Babu PP, et al. Isolation, characterization and differentiation potential of rat bone marrow stromal cells. Neurol India.2010;58(2):201-208.[22] 王峻,吕文辉,刘红云.密度梯度离心与贴壁法分离培养兔骨髓间充质干细胞及其生物学特性观察[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008;12(34):6631-6634.[23] 朱恒,刘元林,陈继德,等.向成骨细胞和成脂肪细胞分化的小鼠骨间充质[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2012,20(5):1187-1190.[24] Guo Z, Li H, Li X, et al. In vitro characteristics and in vivo immunosuppressive activity of compact bone-derived murine mesenchymal progenitor cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24(4): 992-1000.[25] Kitano Y, Radu A, Shaaban A, et al. Selection, enrichment, and culture expansion of murine mesenchymal progenitor cells by retroviral transduction of cycling adherent bone marrow cells. Exp Hematol. 2000;28(12):1460-1469.[26] Tropel P, Noël D, Platet N, et al. Isolation and characterisation of mesenchymal stem cells from adult mouse bone marrow. Exp Cell Res. 2004;295(2):395-406.[27] 包洪卫,孙继芾,王青.巨噬细胞集落刺激因子/核因子KB受体激活物配体体外诱导培养高纯度破骨细胞:最佳剂量探讨[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(2):191-195. |
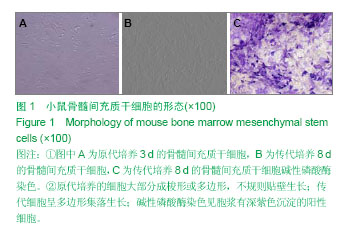
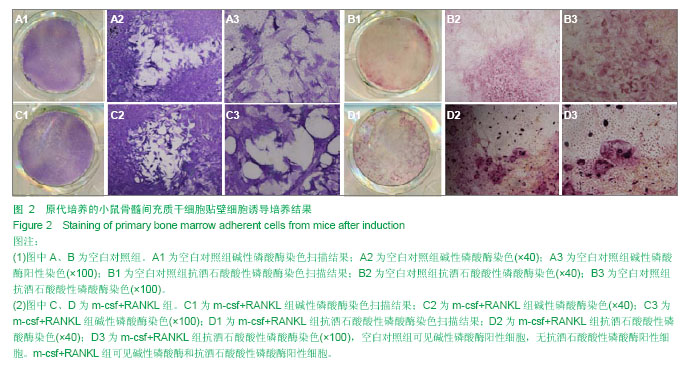
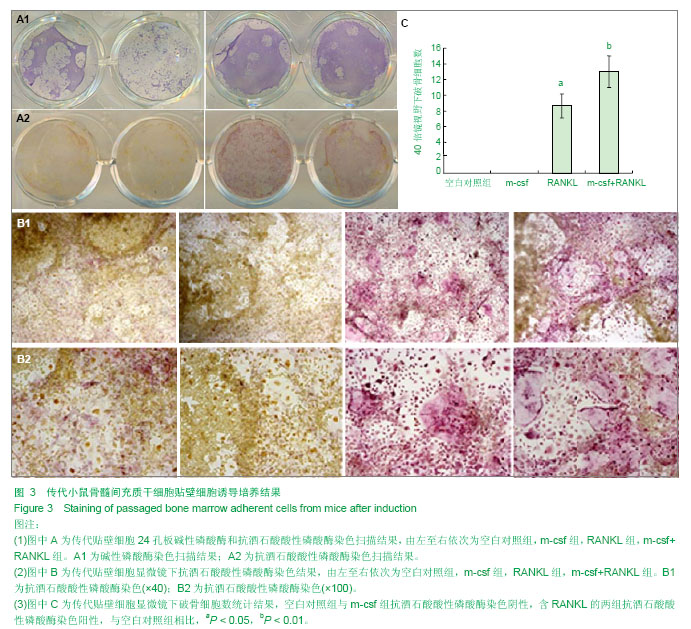
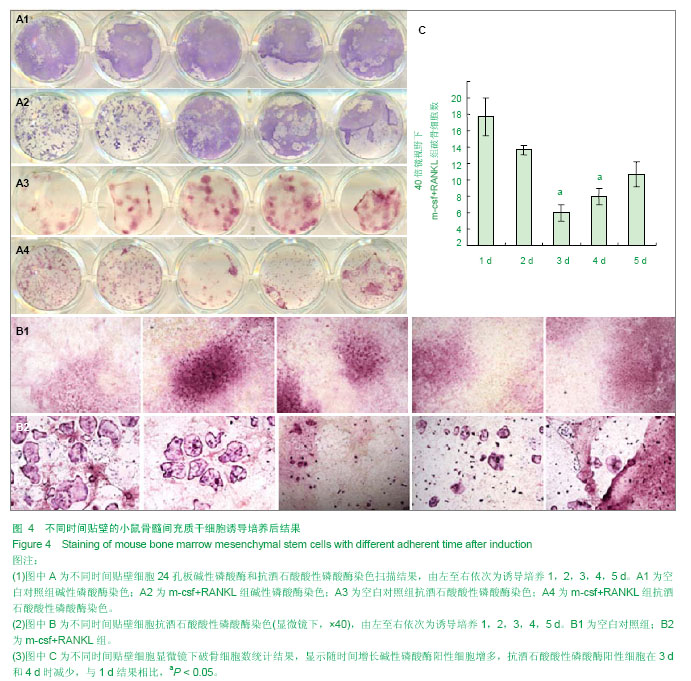
.jpg)